Elasticsearch review: Why developers are choosing Meilisearch for simplicity in 2025
Elasticsearch review: powerful for enterprise scale but complex to manage. See why Meilisearch offers simpler search with same quality results.

Elasticsearch has established itself as the dominant force in enterprise search and analytics, powering everything from website search to log analysis for over 18,000 customers worldwide. With its distributed architecture and comprehensive feature set spanning search, analytics, machine learning, and security, it has become the go-to solution for organizations dealing with massive datasets and complex requirements.
To create this Elasticsearch review, I've analyzed the platform extensively. I believe it's the ideal choice if:
- You need to handle billions of documents across distributed clusters
- You require advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities
- You have dedicated DevOps resources for cluster management
- Your use cases span search, security, and observability
- You need enterprise-grade reliability and support
However, Elasticsearch might not be the best choice if:
- You need a search solution that works well out of the box
- You prefer minimal operational overhead
- Your dataset is in the millions, not billions of documents
- You want to avoid the complexity of distributed systems
- You need flexible pricing options with predictable costs
In this case, you should consider Meilisearch: a modern search engine built on the principle that effective search shouldn’t require a deep knowledge of distributed systems. With its lightning-fast performance, intuitive API, and minimal configuration requirements, it delivers enterprise-quality search results in under 50 milliseconds while being simple enough for a single developer to implement in an afternoon.
Because of that, I've included a detailed look at Meilisearch later in this article, as the best alternative for teams seeking simplicity without sacrificing search quality. If you're ready to explore a more streamlined approach to search, you can try Meilisearch Cloud with a 14-day free trial or deploy the open-source version at no cost.
What is Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is a distributed search and analytics engine built on Apache Lucene, created by Shay Banon and first released in February 2010.
Banon initially started the project in 2004 as a recipe search application called Compass for his wife who was attending culinary school. Realizing the need for a more scalable and user-friendly search solution, he rewrote Compass from the ground up, resulting in Elasticsearch.
The platform has evolved from a pure search engine into a comprehensive data platform.
As the core of the Elastic Stack (formerly ELK Stack), it works seamlessly with Kibana for visualization, Logstash and Beats for data ingestion, creating a complete ecosystem for search-powered solutions. In 2012, Banon co-founded Elastic with Steven Schuurman, Uri Boness, and Simon Willnauer to provide commercial products and services around Elasticsearch.
Today, Elastic positions itself as a "search AI company" with Elasticsearch serving three primary use cases: Enterprise Search for workplace and application search, Observability for log analytics and monitoring, and Security for threat detection and response.
The platform's typical customers include large enterprises, organizations with complex data requirements, teams needing to analyze petabytes of data, and businesses requiring unified search, analytics, and security capabilities.
Elasticsearch pros & cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ Massively scalable distributed architecture | ❌ Complex cluster management requiring expertise |
| ✅ Comprehensive analytics and aggregation capabilities | ❌ Steep learning curve for advanced features |
| ✅ Rich ecosystem with Kibana, Logstash, and Beats | ❌ Resource-intensive, particularly memory |
| ✅ Powerful machine learning and AI features | ❌ Managed cloud limited to 14-day trial |
| ✅ Enterprise-grade security and reliability | ❌ Often overkill for straightforward search needs |
Elasticsearch review: How it works & key features
Distributed architecture and scalability
Elasticsearch's distributed nature is fundamental to its design.
Data is organized into indices, which are divided into shards that can be distributed across multiple nodes in a cluster. Each shard can have replica shards for redundancy, ensuring high availability even when nodes fail. This architecture allows Elasticsearch to scale horizontally by simply adding more nodes to the cluster.
The cluster automatically handles data distribution, rebalancing shards when nodes are added or removed.
A typical production cluster includes master nodes for cluster management, data nodes for storing and searching data, and ingest nodes for pre-processing documents. This separation of concerns allows for optimization based on workload characteristics. Organizations can start with a few nodes and expand to hundreds as their data grows, handling petabytes of information across thousands of indices.
Search and analytics capabilities
At its core, Elasticsearch provides advanced search functionality through its Query DSL (Domain Specific Language), a JSON-based language for constructing complex queries.
The platform supports dozens of query types, from simple match queries to complex geo-spatial searches. Documents are analyzed during indexing through customizable analyzers that handle tokenization, stemming, and synonym expansion.
The aggregations framework enables real-time analytics on stored data. Users can compute metrics like averages and sums, create buckets for grouping data by terms or date ranges, and build pipeline aggregations that work on the output of other aggregations. This framework supports use cases from simple counting to complex statistical analysis.
Time series analysis capabilities include date histogram aggregations for tracking trends and downsampling for summarizing historical data to save storage space.
Machine learning features are integrated directly into the platform, offering anomaly detection for identifying unusual patterns in time-series data, outlier detection for finding unusual data points, and classification and regression for predictive analytics. The platform added vector search capabilities in 2022 for semantic search and Natural Language Processing tasks.
Elastic Stack integration
Elasticsearch gains much of its power from tight integration with other Elastic Stack components.
Kibana provides the visualization layer with interactive dashboards, the Discover tool for exploring data, Canvas for pixel-perfect reports, and Lens for drag-and-drop visualization creation. It also includes alerting capabilities and the Dev Tools console for direct API interaction.
Data ingestion is handled through multiple pathways.
Beats are lightweight data shippers including Filebeat for logs, Metricbeat for metrics, Packetbeat for network data, and others for specific data types. Logstash serves as a more powerful processing pipeline with over 200 plugins for inputs, filters, and outputs. The newer Elastic Agent provides unified data collection with central management through Fleet.
The platform supports webhooks for triggering external actions and provides comprehensive monitoring of the entire stack through Stack Monitoring features.
Where Elasticsearch falls short
While Elasticsearch excels at enterprise-scale search and analytics, several limitations become apparent for many organizations. These constraints reveal a platform optimized for comprehensive capabilities over simplicity.
Operational Complexity: Managing an Elasticsearch cluster requires significant expertise.
Administrators must understand concepts like shards, replicas, and node roles, handle capacity planning and performance tuning, manage index lifecycle policies, and troubleshoot issues like split-brain scenarios. Many organizations find themselves needing dedicated Elasticsearch specialists or expensive consultants, turning what should be a search solution into an ongoing operational challenge.
Resource Demands and Costs: Elasticsearch's memory-intensive nature drives up infrastructure costs significantly.
The platform requires substantial RAM for efficient operation, with recommendations often exceeding available resources for smaller organizations. Combined with the need for multiple nodes for production deployments and the managed cloud service being limited to a 14-day trial, the total cost of ownership can be prohibitive for teams that simply need good search functionality.
Learning Curve Barriers: While basic searches are straightforward, mastering Elasticsearch requires significant time investment. Developers must learn the Query DSL syntax, understand mapping and analysis concepts, grasp aggregation frameworks, and navigate cluster administration. This steep learning curve delays implementation and increases the risk of misconfiguration that can impact performance or stability.
Over-Engineering for Simple Needs: For applications that need search functionality without complex analytics or massive scale, Elasticsearch introduces unnecessary complexity. Setting up a cluster, configuring mappings, tuning analyzers, and managing indices feels excessive when you simply want to add search to a website or application with thousands or millions of documents rather than billions.
Pricing Inflexibility: Unlike modern alternatives that offer both subscription and usage-based pricing models, Elasticsearch's pricing structure can lead to unpredictable costs at scale. Organizations often face surprise overages or find themselves paying for capacity they don't consistently use, making budget planning challenging.

These limitations aren't failures but rather the natural result of building for enterprise scale and comprehensive functionality. However, they create a clear need for alternatives that prioritize developer experience and simplicity without sacrificing search quality.
Top Elasticsearch alternative for simplicity: Meilisearch
Meilisearch addresses Elasticsearch's complexity challenges by taking a different approach: building a search engine that prioritizes ease of use.
Founded by Quentin de Quelen, Clément Renault, and Thomas Payet, Meilisearch emerged from their frustration with existing search solutions while working at large e-commerce companies. They built their search engine from scratch in Rust, focusing on delivering a solution that could be deployed quickly and maintained easily.
Lightning-fast, developer-first design
Meilisearch delivers search results in under 50 milliseconds, making it ideal for search-as-you-type experiences.
This performance comes from its architecture, built entirely in Rust and optimized data structures, including finite state transducers for fast word lookups. The platform uses a Lightning Memory-Mapped Database (LMDB) for efficient storage with low memory overhead.
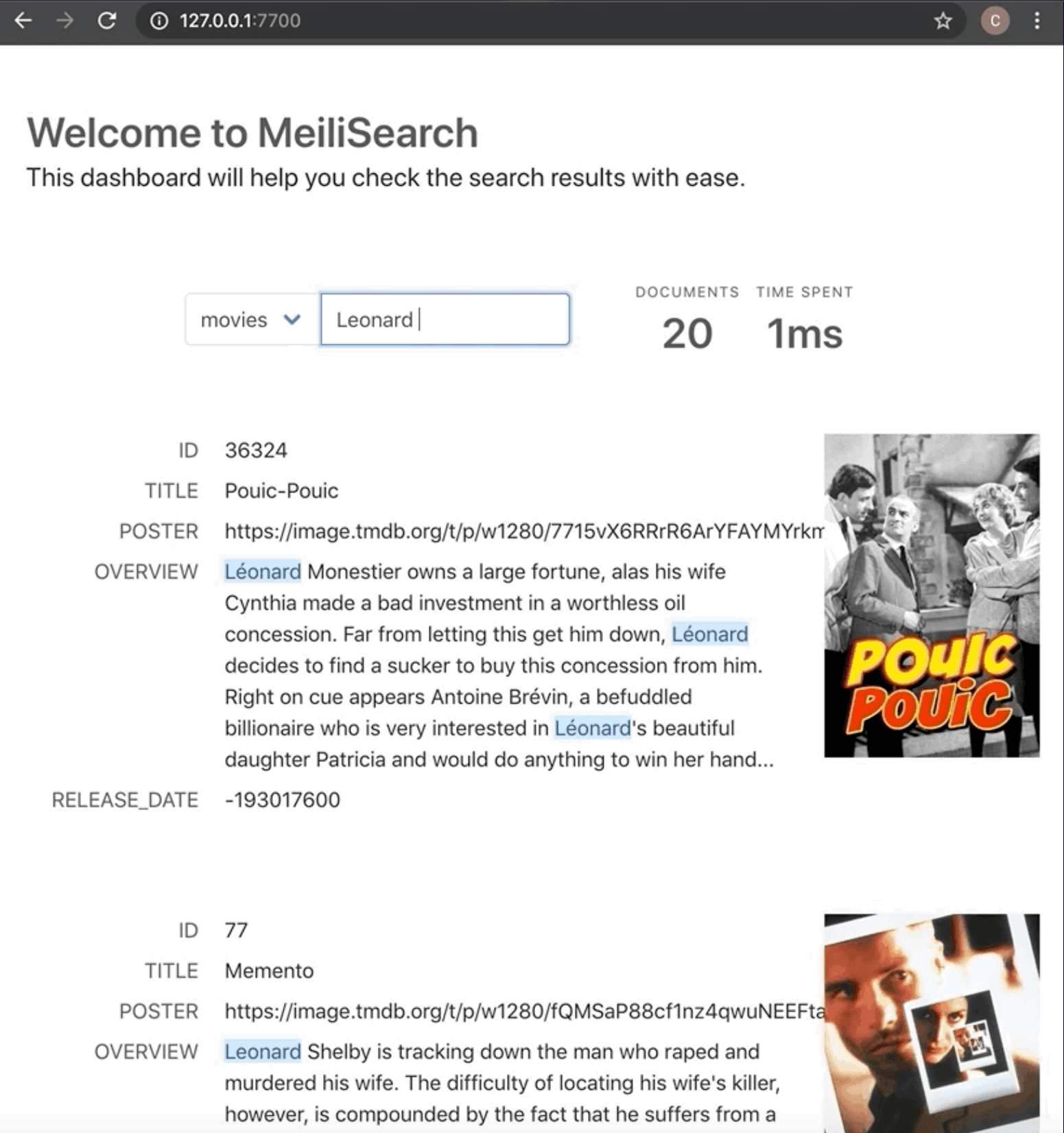
The REST-ful API is intuitive and consistent across all endpoints.
Creating an index, adding documents, and performing searches requires just a few API calls with clear, predictable responses. Official SDKs are available for JavaScript, Python, Ruby, PHP, Go, Rust, Swift, and more, each following language-specific conventions while maintaining API consistency. The web interface provides a dashboard for testing searches without touching code.
 Source: Meilisearch
Source: Meilisearch
Out-of-the-box excellence
Meilisearch provides relevant search results with minimal configuration.
The default ranking rules consider words matched, typo tolerance, proximity of terms, attribute importance, exactness of matches, and sort parameters. These rules work together through a bucket sort algorithm that delivers consistently relevant results across diverse datasets.
Typo tolerance is enabled by default, allowing one typo in words with five or more characters and two typos in words with nine or more characters.
 Source: Meilisearch
Source: Meilisearch
This greatly improves user experience without any configuration. Features like filtering, faceted search, and highlighting work immediately after defining which attributes should be filterable or searchable. There's no need to configure analyzers, tokenizers, or complex mappings.
The platform handles multiple languages automatically through its Charabia tokenizer, supporting Latin, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Thai, and Hebrew scripts. Synonyms and stop words can be defined with simple JSON configurations.
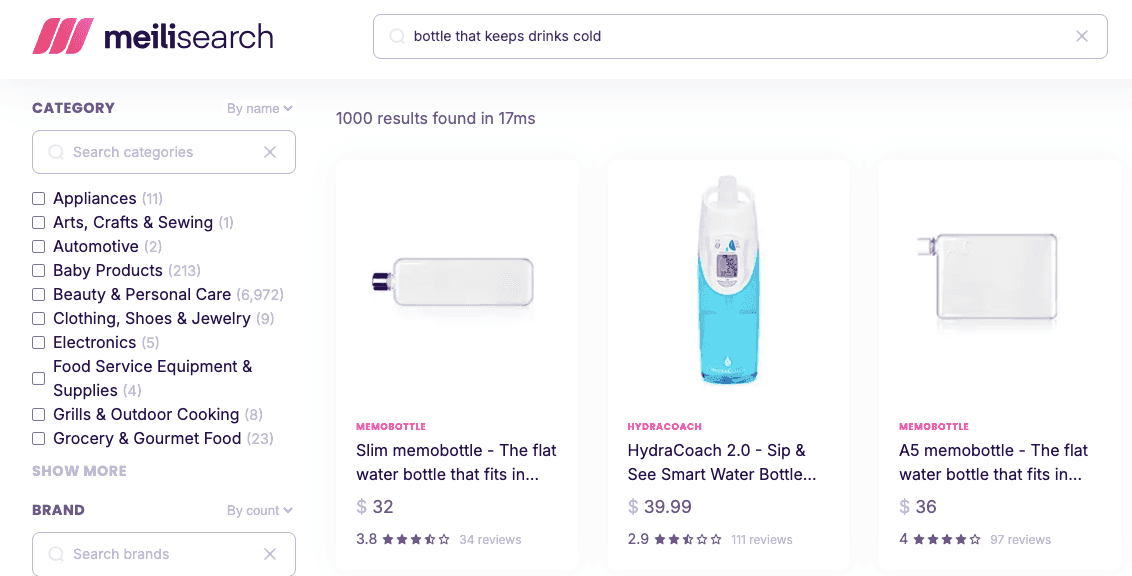
Modern search capabilities
Meilisearch has added AI-powered search capabilities to stay competitive with enterprise platforms.
Hybrid search combines traditional keyword matching with semantic vector search, delivering contextually relevant results even when exact keywords don't match. The platform integrates with OpenAI, Hugging Face, and custom embedding providers through a simple configuration.
 Source: Meilisearch
Source: Meilisearch
Vector search enables semantic understanding of queries, finding documents based on meaning rather than just keywords. Document templates help generate better embeddings by providing context to the AI models. The semanticRatio parameter allows fine-tuning the balance between keyword and semantic results, giving developers precise control over result relevance.
Geosearch capabilities allow filtering and sorting results by geographic location using the _geoRadius filter. Multi-index search enables querying across multiple indexes in a single request with federated results. Tenant tokens provide secure, multi-tenant search where users only see documents they're authorized to access.
Accessible pricing and deployment
Meilisearch is open-source under the MIT license, allowing free use, modification, and distribution.
Self-hosting is straightforward with Docker images, cloud marketplace offerings, and detailed deployment guides for DigitalOcean, AWS, and Kubernetes. A single binary can be downloaded and run without dependencies, getting search running in seconds.
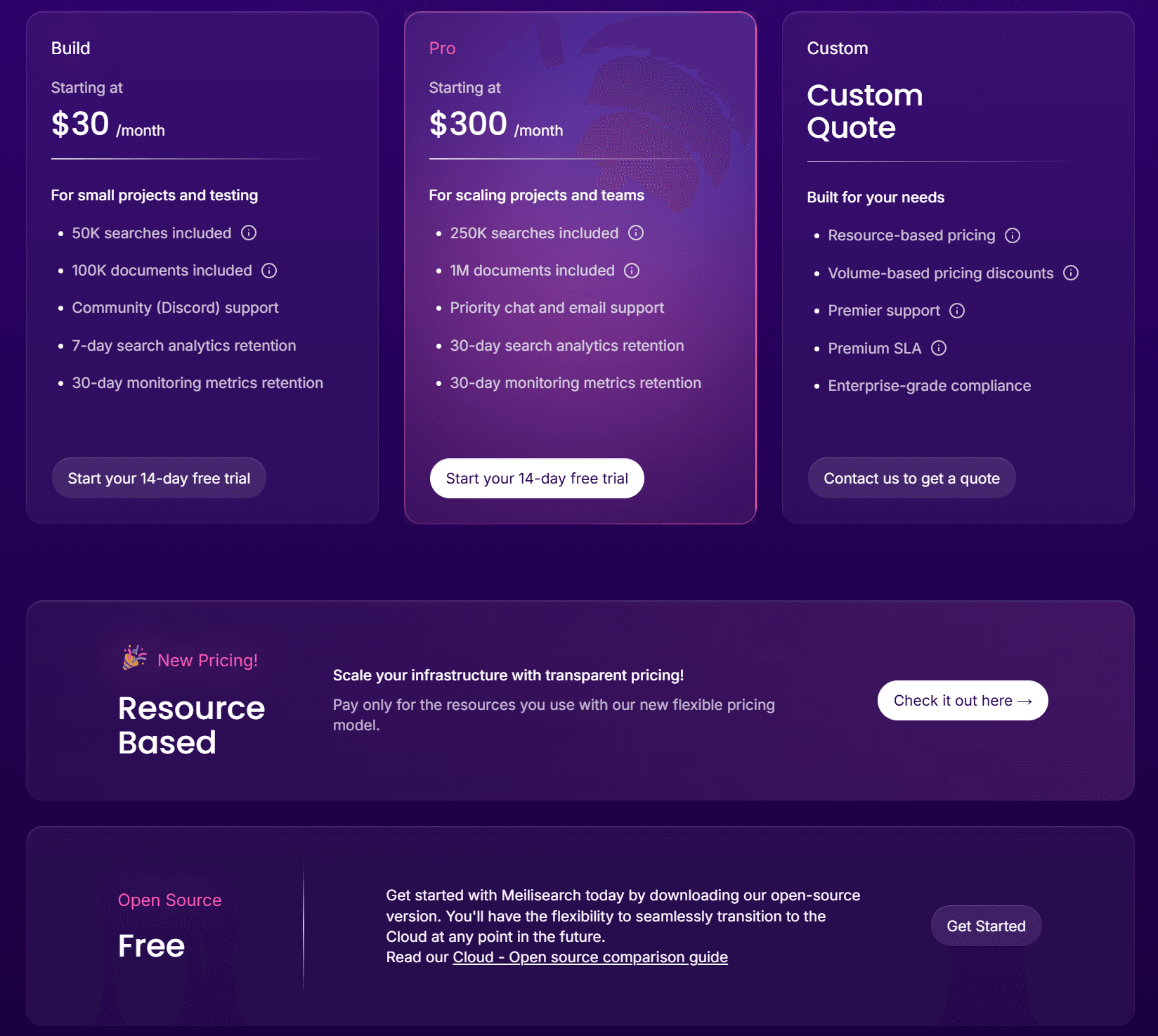
Meilisearch Cloud offers managed hosting with a 14-day free trial, then starting at $30/month for 100,000 documents and 50,000 searches. The Pro plan at $300/month includes 1 million documents and 250,000 searches with priority support. What sets Meilisearch apart is its dual pricing approach: choose between subscription-based plans for predictable monthly costs or resource-based pricing that scales with actual usage. This flexibility means you only pay for what you need, avoiding the surprise overages common with single-model pricing. The open-source version remains free forever for self-managed deployments, though it includes fewer features than the Cloud offering.
The infrastructure requirements are minimal: Meilisearch runs efficiently on a single server, making it cost-effective for most use cases. Memory usage is optimized through LMDB, typically requiring less RAM than Elasticsearch for similar datasets based on community benchmarks.
Elasticsearch or Meilisearch: Comparison summary
| Aspect | Elasticsearch | Meilisearch |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Distributed, multi-node clusters | Single-node (Community); experimental sharding (Enterprise) |
| Setup Complexity | ⭐⭐ Requires planning and configuration | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Works out-of-the-box |
| Learning Curve | Significant time investment needed | Quick to learn and implement |
| Maximum Scale | Billions of documents | Billions of documents (4.3B max per index) |
| Feature Depth | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Comprehensive analytics, ML, security | ⭐⭐⭐ Focused on search excellence |
| Resource Requirements | High memory and CPU needs | Efficient, lightweight operation |
| Free Options | 14-day cloud trial; self-managed open-source | 14-day cloud trial; full open-source version |
| Pricing Flexibility | Single pricing model | Dual model: subscription or resource-based |
| Best For | Enterprise-scale complex requirements | Fast, simple search implementation |
Final verdict
The choice between Elasticsearch and Meilisearch ultimately depends on your organization's complexity requirements and resources.
Choose Elasticsearch if you're building enterprise-scale systems that need more than just search.
It's the right investment when your requirements span multiple domains like security analytics, log aggregation, and machine learning, and when you have the technical team to manage distributed systems. The platform's maturity and comprehensive capabilities make it valuable for organizations where search is part of a larger data strategy.
Get started with Elasticsearch here.
Choose Meilisearch if you want exceptional search without the operational overhead. It's perfect for teams that need to ship search features quickly, value developer productivity, and prefer solutions that work well by default. The combination of fast performance, intuitive APIs, modern AI capabilities, and flexible pricing options makes it ideal for applications where search quality matters but complexity doesn't. The dual pricing model particularly benefits organizations that need cost predictability as they scale.
Get started with Meilisearch here.
Both platforms serve their audiences well. Elasticsearch provides the infrastructure for complex, data-intensive operations at scale. Meilisearch delivers on the promise that great search should be simple to implement and pleasant to use.
Experience search simplicity with Meilisearch Cloud
Ready to implement lightning-fast search without the operational overhead? Meilisearch delivers sub-50ms search results, AI-powered semantic search, and an intuitive API that works out of the box—all with flexible pricing that grows with your needs, not your headaches.


